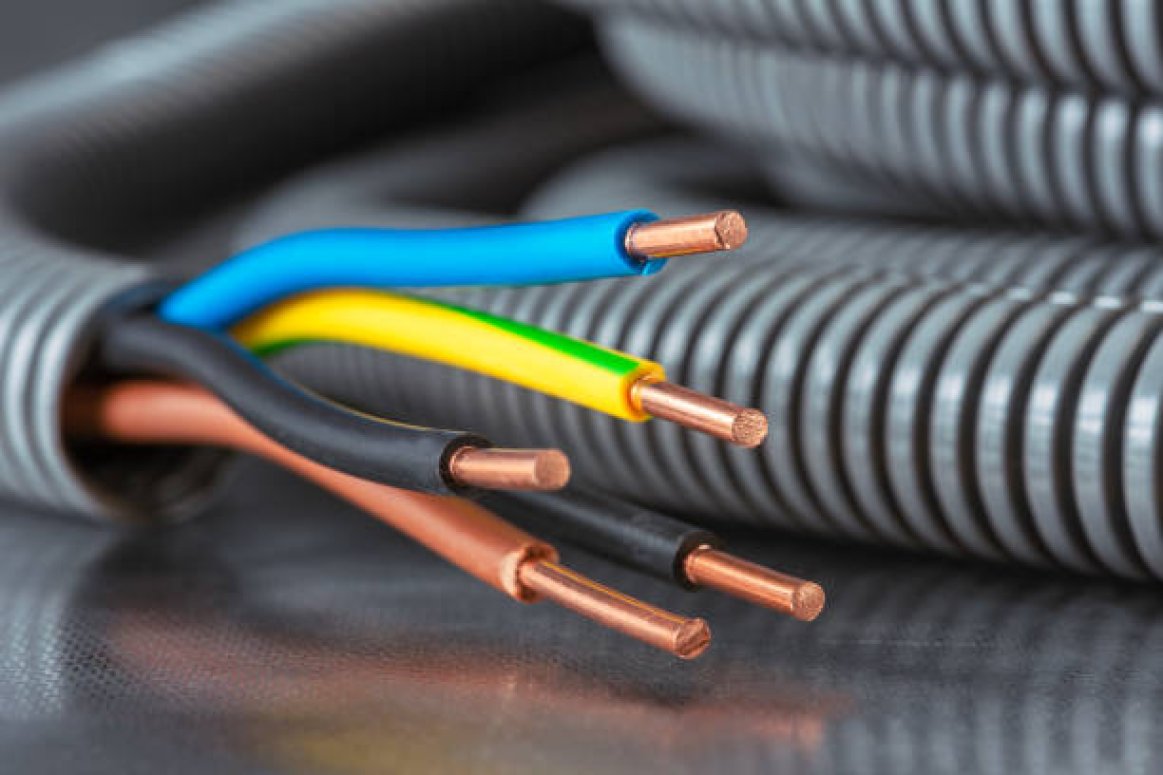

Wire types vary in conductor material and insulation. This is an overview article for wires and conductors that are commonly used in solar pv installations.
Aluminum or Copper: The two common conductor materials used in residential and commercial solar installations are copper and aluminum. Copper has a greater conductivity than aluminum, thus it carries more current than aluminum at the same size.
Aluminum may be weakened during installation especially during bending, however it is less expensive than copper wires. It is not used (not permitted) for interior home wiring, as they are used in larger gauges for underground or overhead service entrances and for commercial operations.
Solid or Stranded: The cable could be solid or stranded, where stranded wires consist of many small wires that allow wire to be flexible. This type is recommended for larger sizes. The current tends to flow on the outside of the wire, thus stranded wires have slightly better conductivity as there is more wire surface.
Insulation: The insulation covering wire can protect the cable from heat, moisture, ultraviolet light or chemicals.
- THHN is commonly used in dry, indoor locations.
- THW, THWN and TW can be used indoors or for wet outdoor applications in conduit.
- UF and USE are good for moist or underground applications.
- PV Wire, USE-2 and RHW-2 cables can be used in outdoor and wet conditions where their outer cabling is UV and moisture resistant. They must be sunlight resistant.
Color: Electrical wire insulation is color coded to designate its function and use. For troubleshooting and repair, understanding the coding is essential. The wiring label differs according to AC or DC current.



Here is a simple table for color coding.
| Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) | ||
| Color | Application | Color | Application |
| Black, Red or Other Color | Un-Grounded Hot | Red | Positive |
| White | Grounded Conductor | White | Negative or Grounded Conductor |
| Green or Bare | Equipment Ground | Green or Bare | Equipment Ground |
For your convenience I have added the table from National Electrical Code that shows conductor applications and insulations. Please refer to NEC Article 310, page 15 - Table 310.13 (.PDF document) for the expanded version of the table.
| Type Letter | Name | Max. Provisions | Application Provisions | Insulation | Outer covering |
| THHN . | Heat Resistant Thermoplastic | 90 C, 194 F | Dry or Damp Locations | Flame retardant, heatresistant thermoplastic | Nylon jacket or equivalent |
| THW | Moisture& Heat Resistant Thermoplastic | 75-90 C, 167-194 F | Dry or Wet Locations | Flame retardant, moisture and heat resistant thermoplastic | None |
| THWN | Moisture& Heat Resistant Thermoplastic | 75 C, 167 F | Dry or Wet Locations | Flame retardant, moisture and heat resistant thermoplastic | Nylon jacket or equivalent |
| TW | Moisture resistant thermoplastic | 60 C, 140 F | Dry or Wet Locations | Flame retardant, moisture resistant thermoplastic | None |
| UF and USE | Underground Feeder & Branch Circuit Cable- Single Conductor | 60-75 C, 140-167 F | See Article 338 and 339: Service Entrance | Moisture and heat resistant | Integral with insulation and Moisture resistant |
| USE-2* and RHW-2* | Moisture resistant thermoplastic and Branch Circuit Cable- Single Conductor | 90 C, 194 F | Dry or Wet and Service Entrance | Moisture and heat resistant | Moisture resistant with insulation |
| PV Wire** | Thicker insulation or jacket to provide additional protection against the abuse that USE-2 wire may receive. | 90 C (194F) wet, 150 C (302 F) dry | Dry or Wet and Service Entrance | Moisture and heat resistant | Moisture resistant with insulation |
*Mentioned as a page note: "Wire types designated with the suffix "2," such as RHW-2, shall be permitted to be used at a continuous 90°C (194°F) operating temperature, wet or dry."
**NEC finds the use of PV Wire adequate and necessary in ungrounded systems.

Comments
Great article. Question, on a residential install, do the wires need to be labeled for the inspection?
The AC cables, metal covered, single-conductor cables, switchboard wires and mineral-insulated wires must be labeled with printed tags.
How do I know what type of insulation my cable has? Will it always be printed on the insulation itself?
According to article 310.11; the wires must be marked with "max. rated voltage", "type of the wire", "AWG size" and "an identification of the manufacturer".
Just wanted to share this forum thread about "PV Wire":
https://www.greentechrenewables.com/forum/8369/what-pv-wire
Very informative post
thanks for sharing this to us