
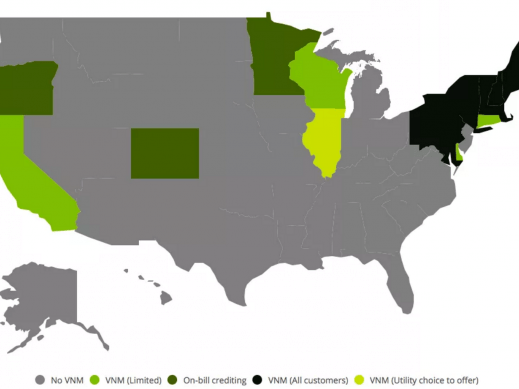
To renewable energy industry professionals, the term VPP might sound familiar. VPP- which stands for Virtual Power Plant – are cloud-based systems that integrate several power sources into one reliable power supply. They can also facilitate the trading and selling of power in the electricity market. According to PRNewswire.com, the virtual power plant model has an estimated compound annual growth rate of 34%, indicating that VPPs will become more readily available to populations in the US, Europe, and Australia.
Projects Becoming Involved in VPPs
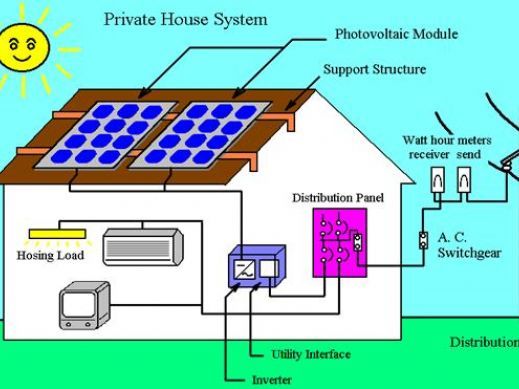
Soleil Lofts is a project in Utah that has become the largest residential virtual power plant in the United States. Soleil Lofts is a partnership between The Wasatch Group, Auric Energy, Sonnen, and Rocky Mountain Power and came together to realize a residential apartment complex that could run on a combination of solar energy and battery storage. The development produces 5.3 megawatts of solar and stores 12.6 megawatts in the battery storage component. This development shows the power of net-zero homes and demonstrates a community approach to stabilizing the power grid through virtual power plants.
Power Generation
The virtual power plant has the benefit of providing sufficient power generation during peak times of the day by forming a cluster of different types of power sources, often including micro combined heating and power, wind power, PV, hydroelectric, backup generators, and energy storage systems. VPPs can replace conventional power plants with their flexibility and efficiency. These systems are sophisticated and require complex optimization and security features, which, like any complicated process, may take time to get up and running smoothly.
Ancillary Services
VPPs are an excellent option for grid operators in maintaining grid stability. These services include frequency regulation, load following, and administering an operating reserve, maintaining the instantaneous balance of electric supply and demand. Currently, ancillary services are controlled by fuel-powered generators. New developments are being made to siphon power from various electric power banks to avoid the need for fossil fuel-powered generators. One example is clusters of electric vehicles that are connected to the grid. The process of charging vehicles would become dynamic based on the individual vehicle's specific charging needs. For instance, the power could be reduced for vehicles approaching a full charge, allowing that energy to be sent to the power grid instead.
Energy Trading
An additional benefit of a VPP is that customers who generate excess electricity could then sell that excess electricity on the open power market. With utilization of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices, information, and communication technologies, a coalition of distributed energy resources (DERs) would allow wholesale electricity markets to interact with a VPP as the intermediary between the DER and the market. The VPP would also mitigate excessive energy prices in competitive markets by reducing demand at peak times.
Further Information
Here is an additional helpful resource for more information. Our Greentech Renewables representatives are also knowledgeable in all aspects of the renewable energy industry. Contact your local Greentech Renewables to start a conversation today.


Comments
Excellent overview! The potential for VPPs is a huge step forward in the maturation of the relationship between renewables and utilities.